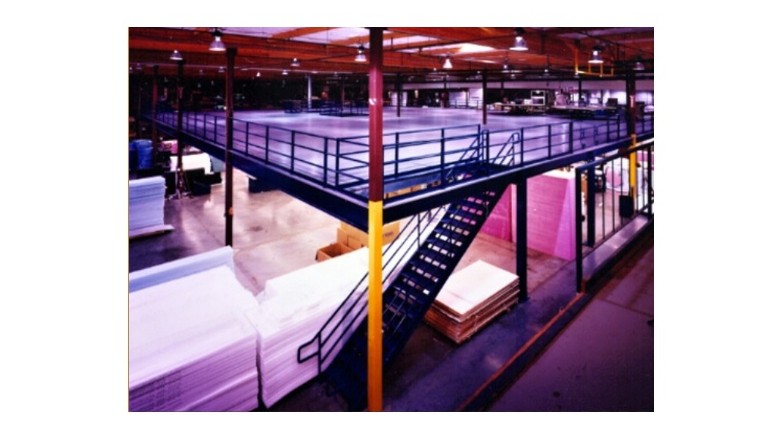
Mezzanines are raised, often un-walled platforms that are used in a diversity of settings; they can store unused materials, provide working space for equipment and seat people in auditoriums, among many other uses. Industrial mezzanines, however, are used only for purposes related to industrial operations. Manufacturers, suppliers, distributors and service companies all make use of mezzanines. Read More…
As a manufacturer of mezzanines, including inplant modular offices, exterior steel buildings, guard buildings, fork liftable and crane liftable buildings, multi-level buildings and mezzanines, Abtech offers turnkey installations or packages for install by end user.
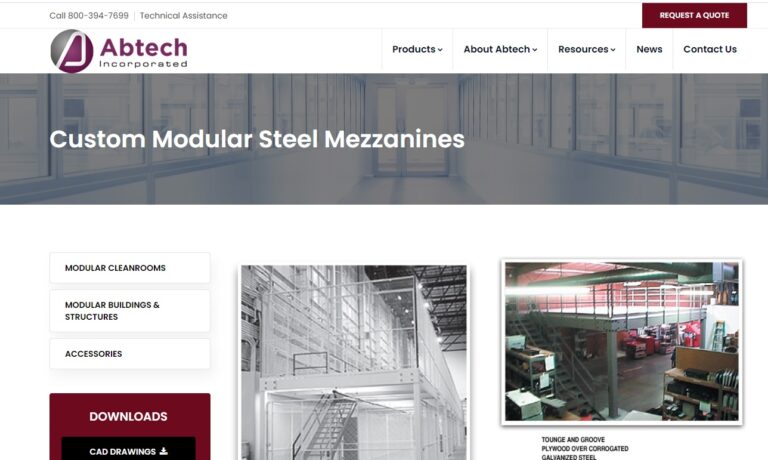
Since 1982, Equipment Roundup Manufacturing has manufactured products such as mezzanines. Our mezzanine structures include mezzanine systems, mezzanine floors, industrial mezzanines & plant mezzanines. Like other customers, you will discover the difference our enthusiastic can-do attitude brings. We help you discover solutions to problems you may not have considered. Your success is our success.

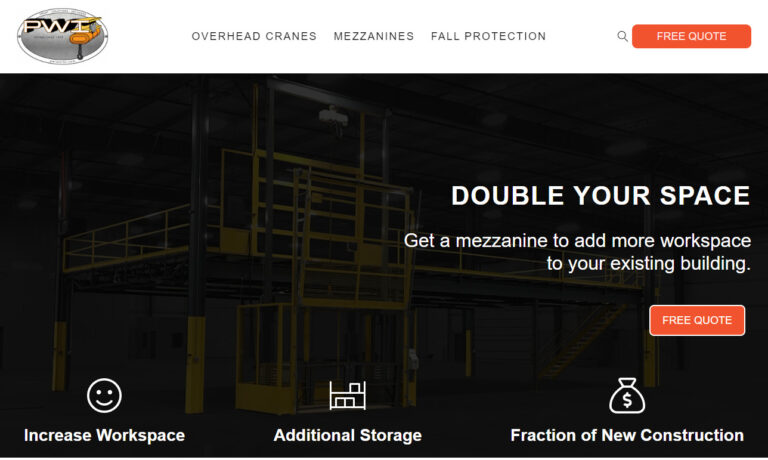
Are you looking for a ready-to-use mezzanine? Our team can handle the design and install so that when we're done, it is ready for you to go to work. When you choose PWI we drastically increase your workspace, in many cases customers create new work or additional storage space. Our steel mezzanines are an affordable alternative to new construction and ensures you are getting the most out of your...
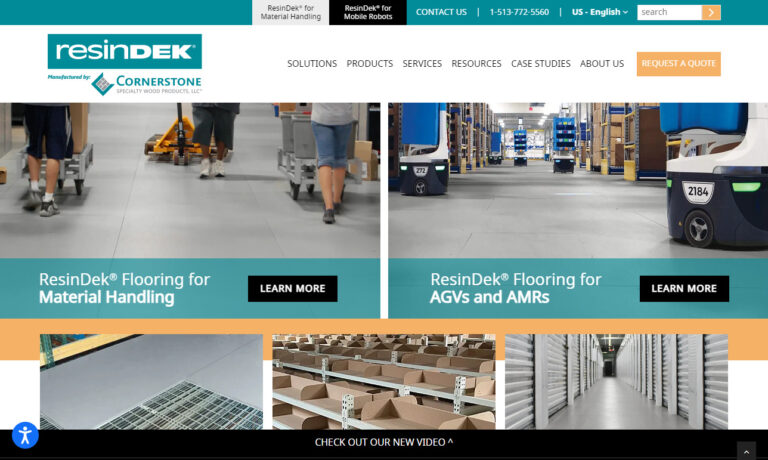
ResinDek® flooring is the solution for mezzanines, work platforms, pick module flooring, and equipment storage. ResinDek® panels have been installed in distribution centers, manufacturing plants, cold storage facilities and many other applications because of its strength, durability, versatility, and variety.
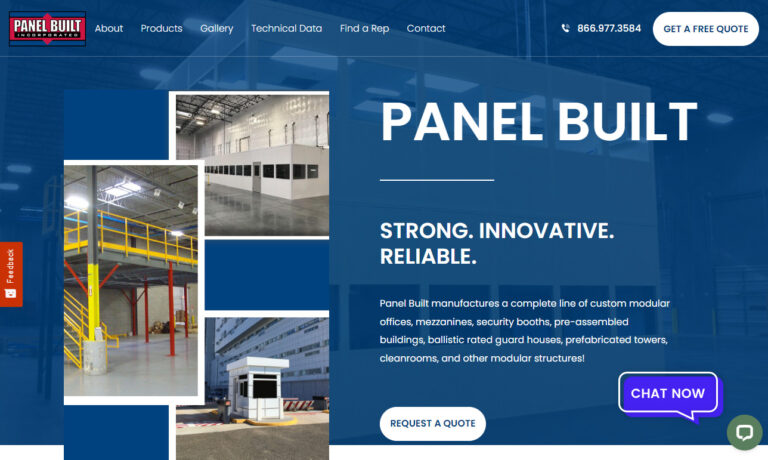
Since 1995 Panel Built has been a leading manufacturer and distributor of industrial mezzanines for many industries. Our high-quality products are durable and have long-lasting performance. All of our products are made in Panel Built’s state of the art facilities. Along with our standard line of mezzanines, Panel Built works with our customers to create custom mezzanines to fit their needs....
Since 1985, Donobrog has been providing low cost easy mezzanines, inplant offices, pick modules, pallet racking and shelving systems…. “Turn Key – New and Used””. Sales, Engineering, Fabrication and Installation. Our labor also can tear down, move, re-assemble and repair existing storage systems. Contact us to discuss your facility improvements.
More Mezzanine Manufacturers
Mezzanine Applications
Mezzanines are versatile structures with a wide range of applications. They can be used for storing unused materials, providing walking space for workers and guests, adding seating in auditoriums, creating additional floor space, and serving as office floors and ceilings. For instance, a small ground-floor office can be constructed beneath a mezzanine, where the mezzanine floor doubles as the office ceiling and a storage platform. Similarly, an in-plant office can be built on top of a mezzanine platform, freeing up the space below for storage or other purposes. Regardless of their configuration, all mezzanine systems prioritize worker safety.
Mezzanines are valuable assets for various service companies, spanning manufacturing, supply, and distribution sectors, as well as non-industrial clients. Industries that benefit from mezzanines include aerospace, agriculture, auto repair and maintenance, education, food and beverage, healthcare, manufacturing, office, outdoor recreation, retail, and transportation.
History of Mezzanines
The term “mezzanine” traces its origins to French, which borrowed it from the Italian word “mezzanino,” a diminutive of “mezzano,” meaning “middle.” Before the Industrial Revolution, mezzanines were mainly found in theaters. However, in the mid-1800s, the advent of the first department stores introduced a new purpose for mezzanines, transforming them into additional store levels. As the Industrial Revolution progressed, manufacturers began incorporating mezzanines into their facilities to optimize storage and create extra usable space. Today, mezzanines continue to serve similar functions but have expanded to various applications and now include features such as conveyors and lifts.
How Mezzanines Work
Modern mezzanines are generally fixed structures, but some are equipped with lift or conveyor systems to move people or items. These systems operate based on commands from automated or semi-automated technology.
What are Mezzanines Used for?
Mezzanines are typically installed in buildings with high ceilings, such as warehouses, offices, and factories. This solution is ideal for companies looking to expand operations without the immediate investment in new buildings. Adding a mezzanine is a cost-effective way to create additional space for offices, storage, and work areas.
Various types of mezzanines are designed for different applications. In industrial settings, they provide extra workspace for light equipment and machinery, including industrial pumps, mist collectors, tanks, HVAC equipment, and conveyor systems. To enhance accessibility and convenience, some mezzanines are engineered with adjustable heights and deck layouts.
When installing a mezzanine, it is crucial to first determine its intended use. This is because key design elements such as load requirements, materials, construction methods, and structural design are all influenced by its purpose.
After establishing the mezzanine’s purpose, the next step is to carefully plan the placement of personnel, walls, and equipment to optimize workflow. When done correctly, a well-planned mezzanine can significantly enhance overall productivity and efficiency.
Common Uses of Mezzanines
Catwalks
Mezzanines can be transformed into catwalk systems, providing an efficient way to transport inventory without disrupting the main production area. This setup allows materials to be moved overhead, keeping them away from the bustling production lines. Additionally, catwalks can be added to link existing mezzanines, further streamlining logistics.
Catwalks are set up by either suspending them from the ceiling or by attaching them to nearby racks and existing mezzanines. These structures offer easy access over tall machinery and equipment. The flooring of a catwalk mezzanine is typically crafted from anti-slip materials such as expanded sheet metals, grated steel, and solid sheets.
Office Space
Certain mezzanine installations are ideal for transforming into office workspaces without compromising the factory floor. Typically located above the production area, they allow supervisors and engineers to stay close to the action. This setup enhances workflow efficiency by positioning workstations near the production zone. Additionally, it is a cost-effective alternative to constructing a new building.
Food Industry
Mezzanines in the food industry are constructed using non-corrosive tubes and food-grade stainless steel, ensuring they are easy to maintain and clean. These mezzanines serve as platforms for cold storage and packaging equipment.
A Platform for Automation Systems
Integrating automation into factories is crucial for advancing the global journey toward Industry 4.0.
Companies with limited space are installing mezzanines to integrate automation seamlessly into their existing factory layouts. This approach allows them to avoid the substantial capital expenditure of constructing an entirely new system. A prime example of this is the installation of overhead conveyor systems, which transport materials autonomously.
Warehousing & Distribution
Modern warehouses boast sophisticated systems for in-house logistics. These efficient facilities employ vertical storage solutions to streamline material handling. By installing a mezzanine, companies can better strategize their inventory management, optimizing both incoming and outgoing goods through the expanded layout.
Mezzanine Types
Due to the diverse range of applications for mezzanines, construction companies provide mezzanine systems in multiple configurations. Here are some examples of the various types of mezzanines available.
Prefabricated Mezzanine
Certain mezzanine applications require nothing more than a compact, straightforward platform for storing supplies or products. In these instances, many operations opt for prefabricated mezzanines. These are pre-designed and partially assembled by manufacturers before customer orders are even placed.
Structural Mezzanine
Structural mezzanines are elevated platforms supported by a mix of the building’s load-bearing structures and additional columns or supports. They can serve as work surfaces for machinery or as storage areas for heavy materials. Typically, structural mezzanines are incorporated into the building during its construction, with their design and purpose pre-planned to meet specific needs.
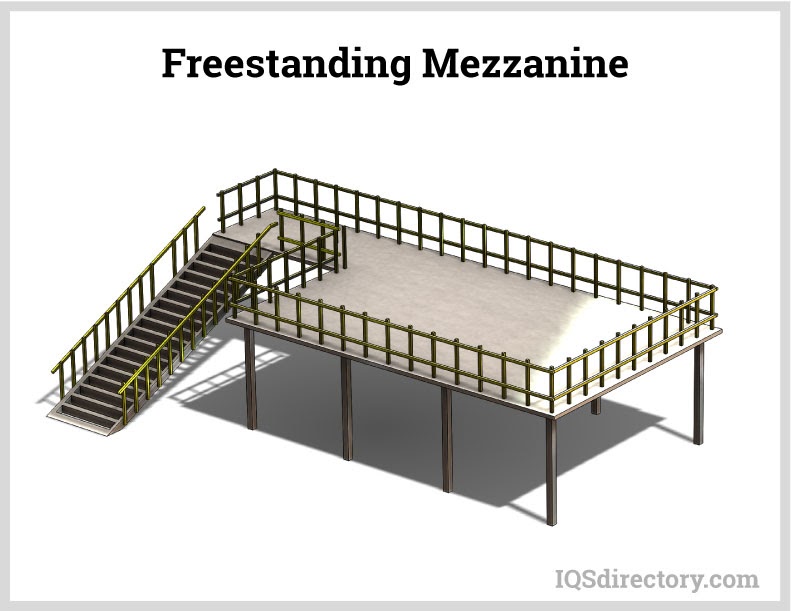
Free Standing Mezzanine
Freestanding mezzanines, also known as equipment platforms, are typically prefabricated structures that stand independently without relying on wall support. Due to this design, they are often utilized for lighter tasks, such as temporarily storing lightweight materials. One significant benefit of both freestanding and structural mezzanines is that they do not obstruct workers or machinery on lower levels. The supports can be strategically positioned to minimize any disruption to the movement of personnel and equipment.
Free-standing mezzanines are often utilized as equipment platforms, standing independently from the building’s main structure. Their flexibility allows them to be reconfigured as needed. For added stability, their posts can be anchored to the floor.
Perimeter Mezzanine
Perimeter mezzanines are commonly found in factories, warehouses, and other expansive buildings. They provide an excellent vantage point for observing floor operations and facilitate quick movement across a busy or crowded space. Their convenience also makes them ideal for short-term product storage. Additionally, perimeter mezzanines can host visitors or guests during tours. To further aid in transporting products and people, these mezzanines can be outfitted with lift and conveyor systems.
Catwalk Mezzanines
These are installed in warehouses to enhance the capacity of tall racks. The current shelves act as a foundation for the mezzanine structure, and additional support columns can be added to bolster stability between the shelves.
Installation of Mezzanines
While installing mezzanines can be quick, several factors need to be addressed beforehand. First, evaluate the building’s structure to ensure it can support the added weight and check for any space constraints. Next, decide whether you prefer a permanent or temporary mezzanine. Lastly, and most crucially, ensure compliance with the regulations set by the International Building Code (IBC) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
Mezzanine Equipment Components
Mezzanines consist of base plates, columns, braces, and various other hardware components.
Base plates are essential for the stability of mezzanines. They control lateral and deflection movements, ensuring the structure remains secure. Standard mezzanines feature base plates measuring 12 inches by 4 inches, anchored firmly by bolts. Columns support the mezzanine levels, providing strength against vertical, horizontal, and twisting forces. Braces and additional hardware enhance the overall structural integrity by reducing lateral movement. Manufacturers often assemble these structures using nuts and bolts for added stability.
Benefits of Mezzanines
Mezzanines offer a multitude of advantages to their users. Firstly, their incredible versatility allows them to serve various purposes, from additional storage space to pallet rack storage. Manufacturers can customize mezzanine systems to fit almost any environment, and this adaptability also means they come in a wide range of prices. Adding a mezzanine to your facility effectively doubles your available work and storage space, with even larger models providing even more capacity. Many mezzanine systems are modular, allowing them to be easily disassembled, expanded, reduced, or relocated as needed. Additionally, mezzanines provide a way to transform your workspace without significant construction costs or extended downtime, as they can be installed within days rather than weeks or months.
Mezzanine Design and Customization
Manufacturers construct mezzanines using various materials, including structural steel, stainless steel, cold rolled steel, and hot rolled steel. They might also utilize fiberglass or aluminum, while for non-industrial uses, wood or composite lumber is an option. For LEED certified warehouses aiming to reduce reliance on structural steel and non-recycled materials, recycled composite lumber panels are often employed. When selecting a material, manufacturers consider whether it needs to be free-standing, capable of standing independently, or structural, serving as an integral part of the building. Lightweight materials like aluminum are chosen for mezzanines that won’t bear heavy loads, while fiberglass is ideal for decking in corrosive environments.
When designing, manufacturers plan the mezzanine floor layout and determine additional necessary features. These can include shelving, pallet racks, decks, floor perforations, stairs, railings, conveyor lifts, and more. Safety is a top priority in mezzanine construction; access stairs typically have treads and are marked with bright or reflective tape to minimize slipping or stumbling. Perimeter railings are also installed to prevent falls.
When a mezzanine needs to serve a specialized function, manufacturers will design a custom mezzanine tailored to your exact requirements. This could include unique floor perforation sizes or shapes, or an unconventional perimeter.
Safety and Compliance Standards of Mezzanines
Generally, mezzanines adhere to the International Building Code, which specifies that a mezzanine can occupy up to one-third of the floor space of the level below it. Multiple mezzanines are allowed in a space as long as their combined area does not exceed one-third of the total floor space. It’s important to note that local building codes may have different requirements. In the USA, industrial mezzanines must also comply with OSHA’s safety standards. Additionally, if you want your mezzanine to be accessible, it must meet ADA standards.
Things to Consider Regarding Mezzanines
Mezzanines offer a cost-effective solution for increasing a building’s working space without expanding its footprint. They create ideal areas for offices, additional storage for inventory, and platforms for light equipment. Often referred to as miscellaneous floors above the ground level in various industries, mezzanines can be customized and installed based on available space, intended use, and the building’s construction.
Similar to any construction project, mezzanine installations are governed by various standards to ensure quality and safety. Before deciding to install a mezzanine, it is crucial to consider its intended use, whether for office space, storage, manufacturing, or equipment placement.
Load Requirements
The load requirements for mezzanine construction depend on its intended use. Mezzanine weight ratings are measured in force per unit area (e.g., kN/m²). Light usage has lower load requirements, while heavy-duty applications need higher load capacities. Typical ratings are:
- Office space: 3.5 kN/m²
- Light stockroom: 4.8 kN/m²
- Medium stockroom: 7.2 kN/m²
- Heavy stockroom: 9.6 kN/m²
Slab Capacity
The feasibility and safety of mezzanine construction are determined by the slab’s capacity. This capacity also influences the choice of columns and footings required to support the mezzanine. Typically, standard slabs, which are six to eight inches thick, can support up to 25,000 pounds.
Construction of Stairways and Handrails
The design and inclusion of stairways and handrails on mezzanines are regulated by safety standards established by various associations, ensuring the well-being of workers. These features are crucial for maintaining a safe working environment. The specific design and construction of handrails and stairways depend on the intended use of the mezzanines. For example, a common guideline for stairways is to include anti-skid elements like expanded metal sheets or diamond-patterned steps.
Surface
There are numerous options for constructing mezzanine floors, including steel, grating, diamond plate, high-density particleboard, and concrete.
Building and Construction Codes
The mezzanine installation must comply with the standards established by various safety organizations, such as the International Building Code (IBC) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration. These regulations may differ based on local government requirements.
Installing a mezzanine is an excellent way to maximize space and save money. However, choosing the wrong manufacturer can lead to significant headaches and budget overruns. To help you avoid these pitfalls, we’ve compiled a list of experienced and reliable mezzanine manufacturers. You’ll find profiles of these top companies throughout the page. When you’re ready to start your search, take some time to read through these profiles. Visit their websites to gather more information. As you browse, consider factors such as application suitability, specifications, and price range. Select three or four manufacturers you’d like to contact directly for quotes or consultations. After speaking with your selected companies, compare their responses carefully. Evaluate which manufacturer can provide the customizations, standards, pricing, delivery services, and overall customer service that best meet your needs.





 55 Gallon Drums
55 Gallon Drums Floor Gratings
Floor Gratings Mezzanines
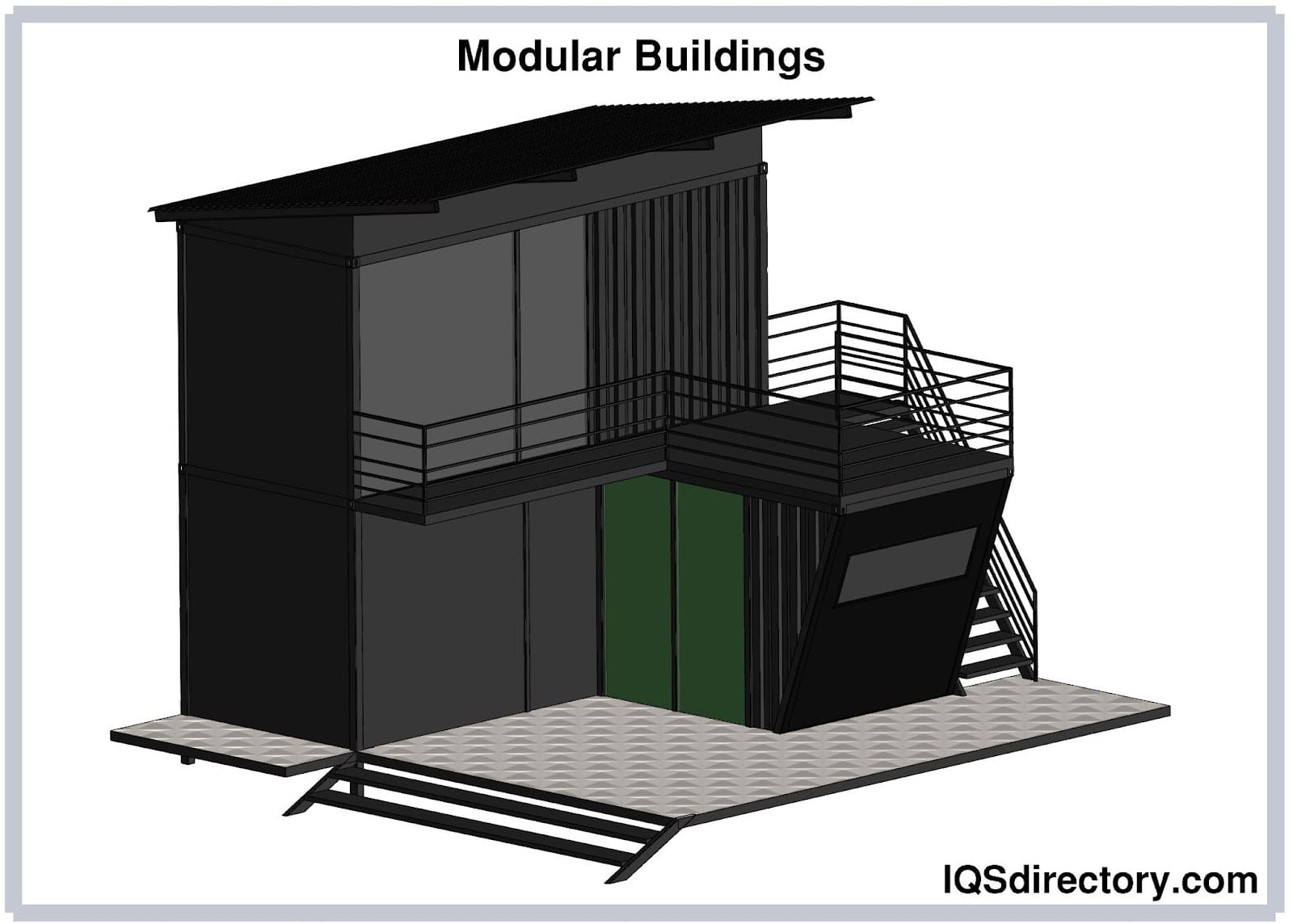
Mezzanines Modular Buildings
Modular Buildings Plastic Containers
Plastic Containers Plastic Pallets
Plastic Pallets Plastic Tanks
Plastic Tanks Steel Shelving
Steel Shelving Stainless Steel Tanks
Stainless Steel Tanks Storage Racks
Storage Racks Work Benches
Work Benches Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services